In fact, this technology, which first started as Bitcoin Mining, can be summarised as solving complex mathematical problems on the blockchain by means of special hardware devices, video cards, etc. and being rewarded with the crypto asset in return for the approved crypto asset transactions.
The process in Bitcoin mining proceeds as follows:
– Verification of Bitcoin blocks using the processing power of devices
– Adding Bitcoin blocks to the chain
– It covers the processes of generating and distributing Bitcoins as a reward in return.
People who produce bitcoins are called miners. The Bitcoin block actually proceeds by being confirmed by multiple verifications. However, the first miner to verify the block is entitled to receive the reward. The best part of blockchain technology is; All transactions performed on the blockchain are recorded as of the first block. It is the fallacy that “transactions are confidential”, which is always confused here and is often used by those who commit fraud on the site. The issue to be known here is this: All transfers made on the blockchain are “anonymous” but not completely confidential. And if anonymous transfers have KYC verification, the wallet owner can be identified.
Some of the coins that are still mined ;
-KASPA
-BİTCOİN
– TEZOS etc.


It can be defined as games integrated into blockchains, which we can characterise as play and win. Play to Earn games allow players to convert in-game special items, crypto assets or in-game currencies into real money by swapping the games they play digitally for tokens. At the same time, it is possible to contribute to the crypto asset tokenomic balance with Play to Earn games. Namely; mechanisms such as burning etc. in the generated crypto asset codes can be activated thanks to these games. Thanks to blockchain-integrated games, crypto asset holders and those considering investing remain actively involved in the project. Crypto-asset teams thus have the opportunity to move forward the sustainability of the value they create.
Some of the PLAY TO EARN Crypto Assets
AXS – MANA – TLM – SHRAP
What is a limit order and how to use it?
Limit order is a method used by crypto asset investors who do not actually want to make instant purchases; It is a method used by crypto asset investors who intend to buy when it comes to the price they want or sell when it comes to the price they want. Especially conscious crypto asset investors; taking into account many metrics such as technical analysis, news follow-up, developments related to the crypto asset in question, determine a suitable purchase or sale location and give limit order instructions from these figures. The Limit Order concept, which is mostly encountered in centralised crypto exchanges, has recently started to be used in decentralised Dex exchanges
It is the type of order executed by investors who want to trade on crypto exchanges at instant price. When you want to sell your crypto asset, you sell it at the highest market figure given instantly. On the contrary, when you want to make a purchase, you instantly make your purchase at the lowest price in the market.
Market order is a method frequently used by both professionals and novice traders. However, a wrong instruction given by investors who are excited by rapid price movements may result in the crypto asset they want to buy more expensive and the crypto asset they want to sell cheaper. Traders using market orders should therefore be more careful when opening trades.


Halving literally means halving. In cryptoassets that are mined, the reward per block is halved periodically and mining becomes more difficult at each halving period. This halves earnings for miners, while the reduction in supply aims to maintain price stability.
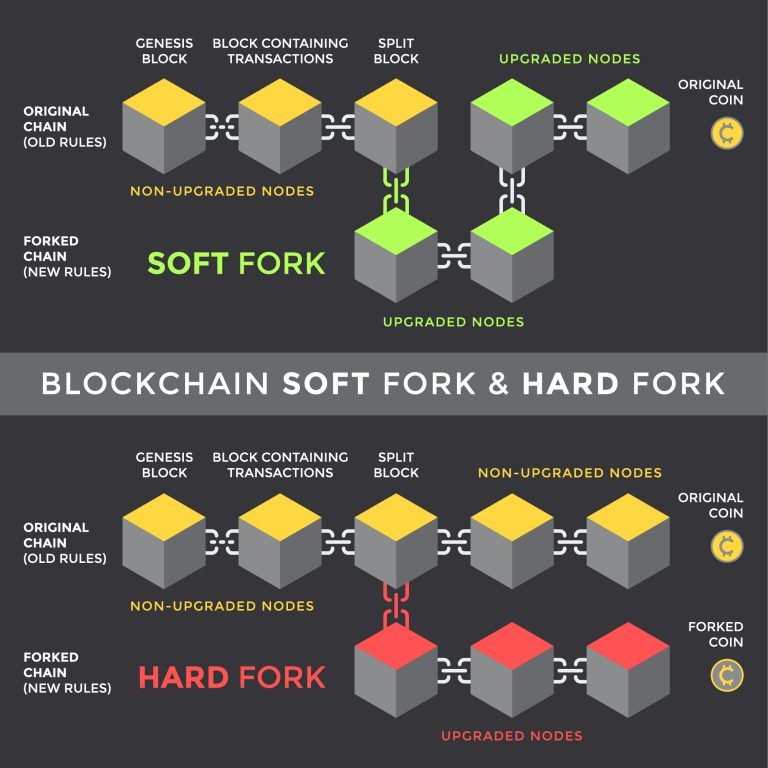
The term fork can be referred to as “bifurcation”. With bifurcation, the crypto asset is converted into separate copies on the existing blockchain networks to which it is connected. It would not be correct to characterise the bifurcation as a complete separation. In a way, we can call them versions of the copy in different networks. There may be more than one reason behind the preference for forking in crypto assets. Some of these are;
Elimination of an error in the system
Correction of errors in the current system
A different technology integration
Speed
Reduction or increase of transfer payments, etc;
Arbitrage, in fact, is a phrase that is frequently used wherever there is finance. On the crypto asset side, arbitrage can be defined as the act of buying a crypto asset instantly in the market and selling it at a higher price in another market and making a profit as much as the price difference between them.
Crypto asset markets are markets with high risk appetite, which draw an extremely volatile market image. Therefore, crypto asset investors have to be very careful about making profits through arbitrage. In particular, there are many individuals and institutions that will manipulate the market both on a global and local basis. Otherwise, an arbitrage transaction opened with the aim of making a profit may result in unexpected losses.
Fud consists of the initials of the words “Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt” and means “Fear, uncertainty, and doubt” in Turkish. In the crypto sector, it is one of the methods of reducing the value of crypto assets and collecting assets in the hands of unconscious investors cheaper through manipulation. With FUD, however, the aim is not only to accumulate cheap assets. Sometimes FUD posts are also made by different crypto asset teams or investors with similar technology or promises. Crypto assets, which are not yet regulated on a global and local basis, can unfortunately cause losses to the investor with speculative fuds. However, the fact that crypto assets are not regulated will not prevent it from being considered as an asset class, and if the investor who has been unjustly and deliberately harmed shows the courage to take legal action, he will be able to get positive results for the compensation of his losses.
Elimination of an error in the system
Correction of errors in the current system
A different technology integration
Speed
Reduction or increase of transfer payments, etc;
NFT stands for “Non Fungible Token”, which can be translated as “Non-Fungible Token” or “Money that cannot be changed”. NFTs are actually crypto asset units. But rather than the classic crypto assets, we can include anything digital or digitised in the definition of NFT. For example, it can be a digital copy of a picture your child has drawn in a drawing book, a photo on your phone, a social media post and many more. What distinguishes NFT from other assets known and referred to as “cryptocurrencies” is the definition of “uniqueness”. Because each NFT is bought and sold as unique. Just as there is only one painting of the Mona Lisa or only one title deed to a person. Simply put, an NFT is a digital asset that has a value and is collectible.

Proof of work, proof of work, or PoW protocol for short, is a system that aims to prevent misuse of services such as denial-of-service (DOS) attacks and spam messages.
Denial-of-service is a cyber-attack that temporarily or indefinitely disrupts the host, a service provided by powerful servers connected to the Internet, with the aim of preventing the use of a machine or network resources by actual users. DoS attacks, known to many people by the abbreviated name Denial-of-service, are caused by throwing too many unnecessary process requests to a machine or network servers, causing the machine to crash as a result of overload. Proof-of-work (PoW) is basically designed to prevent all cyber-attacks that will adversely affect the operation of systems, such as the cyber-attacks mentioned above.
So what is the place of Proof Of Work in blockchain technology?
Proof of Work, which started to be used in blockchain technology with Bitcoin, allows crypto assets in payment systems to work without central authority, to be kept and approved. Thus, thanks to the protocol, at least 51 per cent of the computing power in the network must be compromised for attacks on the Bitcoin network to be successful. Although this is considered very unlikely or even impossible, in 2017 the mining pool owned by mining equipment manufacturer Bitmain managed to reach 45 per cent of the network’s processing power. Although 51% seems to be the biggest advantage of the PoW protocol, it is also a fact that this may lead to monopolisation, which is a handicap that appears to be an advantage. If the Bitcoin phenomenon, whose purpose of emergence is decentralisation, loses its 51% transaction power to a monopoly, then it is also possible that decentralisation will be completely eliminated. Another handicap is that systems based on the PROOF OF WORK protocol require high processing power and require very intensive energy use. This situation not only causes high costs but also keeps the agenda busy as an issue on the radar of climate activists.
The POS protocol, which we met after the POW protocol, is primarily an environmentally friendly protocol. The sine qua non of this protocol is the presence of NODs. The POS protocol has a mechanism to reward those who hold a crypto asset, do not sell it, lock it in the system for a certain or indefinite period of time with the staking mechanism it offers. The similarity to the POW system is that it aims for decentralisation, the difference is that decentralisation is achieved not through miners but through Nodes and holders that lock assets to these Nodes. Although setting up a Nod on a network requires technical knowledge and hardware, it is a fairly simple method to become a staker (token locker) of a Nod. However, the important issue in this method is that Nod is a competent person in terms of both reliability and technical equipment. This is because the nodes on the network are resolved through the Nodes and the rewards are sent to the Nodes and then to the stakers. If the Nodes whose assets are locked by the stakers do not follow an update on the network, for example, and do not integrate their Nodes into the update, they will be penalised by the network and will not receive rewards. In this case, the stakers who stake to Nod do not actually receive the staking rewards they should deserve.
It may make more sense to stake on a high-volume crypto exchange instead of staking directly on Nodes. Because the Nodes of these exchanges can follow the integration into the network instantly. Of course, here, too, the question of how secure a centralised exchange can be may leave a question mark.
To summarise the issue; POS protocol appears as less energy and less laborious work than POW protocol, even as a passive income mechanism. Again, it is a more robust system against the realisation of the 51% attack we mentioned in POW. A large number of wallet holders with the lure of passive income would somehow serve decentralisation, which in turn would increase network security to the extreme.
Launchpads provide access to early-stage crypto projects and make it easier for investors to invest in these projects. Projects offer the crypto assets of the project for a certain period of time through the launchpad platform. Investors can support the project by purchasing these crypto assets.
Launchpads generally require pre-registration for crypto asset sales. Crypto-asset trading platforms can request payment in crypto-asset units that they themselves produce. Thus, investors obtain the crypto asset of the project even before it is listed and have the potential to earn serious income depending on the success of the project in the future.
Launchpads make it easier for new and innovative crypto projects to access financing, while offering investors the opportunity to invest in early-stage projects.
Of course, there are some issues to be considered in this regard. Although Launchpad platforms have done the necessary research for the projects they will offer for sale within their structure or claim that they have done these researches, participants can be victimised and defrauded by the project team to be sold or Launchpad-Project team contractual methods. Although the victims accept the damage in these matters, they can recover their losses through a legal investigation and contribute to the judiciary in punishing those concerned.
Kripto varlıkla ilgili hukuki sorununuz varsa veya yatırım tavsiyesi içermeyen teknik bilgi almak istiyorsanız iletşime geçin